将 Webhook 处理卸载到队列
在 Web 应用程序中,通常希望将客户端不需要即时响应的异步任务处理卸载到队列中。这样做可以保持您的 Web 应用程序快速响应,而不是占用宝贵的资源等待长时间运行的进程完成。
您可能希望部署此技术的一个场景是处理 Webhook。在收到不需要响应的非人类客户端发出的 Webhook 请求后,您可以立即将该工作卸载到队列中,以便更高效地处理。
在本教程中,我们将向您展示如何在处理 GitHub 仓库的 Webhook 请求时执行此技术。
在 Playground 中尝试 跳到标题
✏️ 查看此 Playground,它实现了 GitHub 仓库 Webhook 处理程序。
使用 Deno Deploy Playground,您可以立即部署自己的 GitHub Webhook 处理程序,该程序同时使用队列和 Deno KV。我们稍后将逐步讲解此代码的功能。
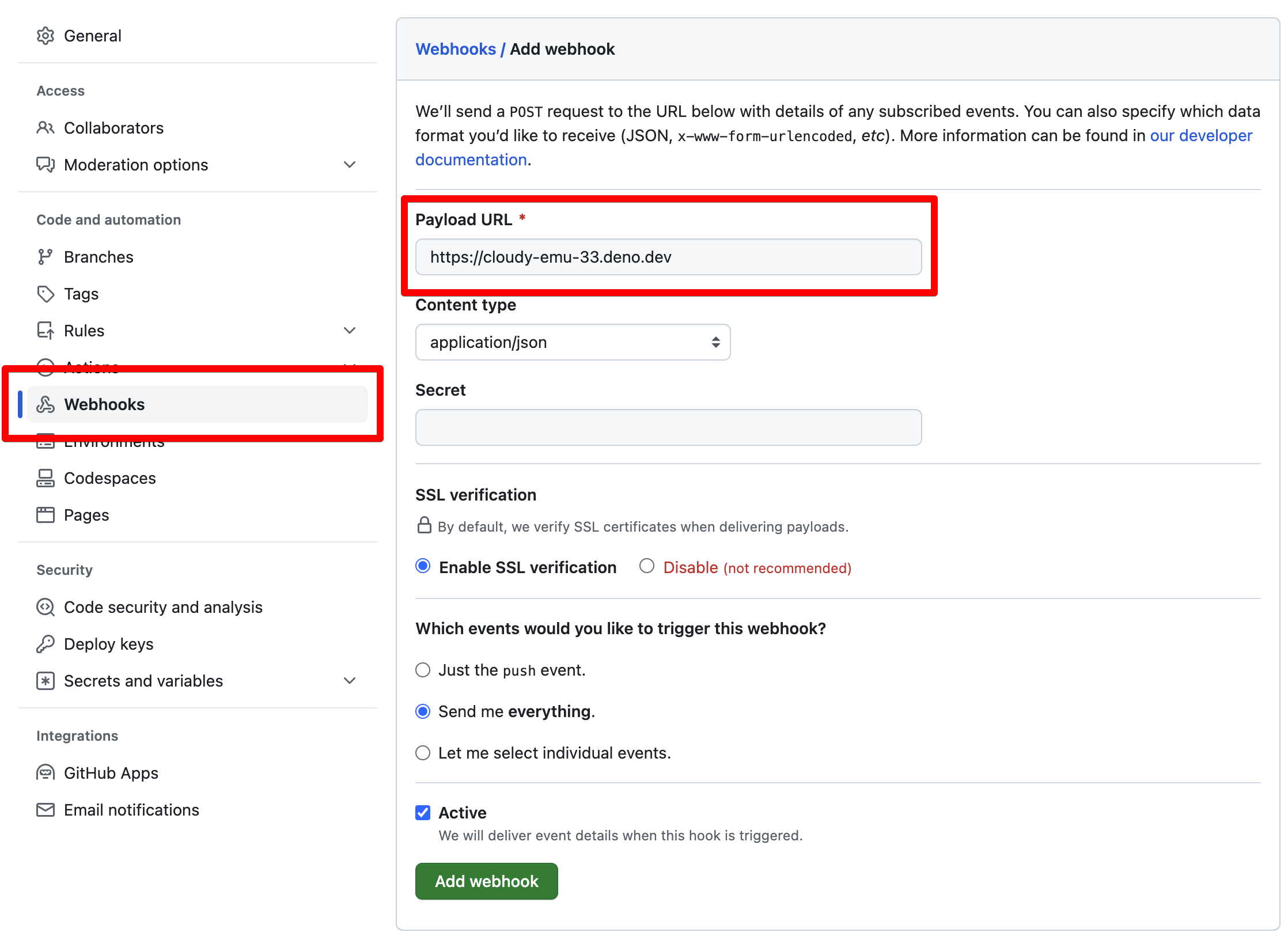
为仓库配置 GitHub Webhook 跳到标题
要尝试您刚在 Playground 中启动的 Webhook,请为您控制的 GitHub 仓库设置新的 Webhook 配置。您可以在仓库的“Settings”(设置)下找到 Webhook 配置。
代码演练 跳到标题
我们的 Webhook 处理函数相对简单——不含注释,总共只有 23 行代码。它连接到 Deno KV 数据库,设置一个队列监听器来处理传入消息,并使用 Deno.serve 设置一个简单服务器来响应传入的 Webhook 请求。
请阅读下面的注释,了解每个步骤中发生的情况。
server.ts
// Get a handle for a Deno KV database instance. KV is built in to the Deno
// runtime, and is available with zero config both locally and on Deno Deploy
const kv = await Deno.openKv();
// Set up a listener that will handle work that is offloaded from our server.
// In this case, it's just going to add incoming webhook payloads to a KV
// database, with a timestamp.
kv.listenQueue(async (message) => {
await kv.set(["github", Date.now()], message);
});
// This is a simple HTTP server that will handle incoming POST requests from
// GitHub webhooks.
Deno.serve(async (req: Request) => {
if (req.method === "POST") {
// GitHub sends webhook requests as POST requests to your server. You can
// configure GitHub to send JSON in the POST body, which you can then parse
// from the request object.
const payload = await req.json();
await kv.enqueue(payload);
return new Response("", { status: 200 });
} else {
// If the server is handling a GET request, this will just list out all the
// webhook events that have been recorded in our KV database.
const iter = kv.list<string>({ prefix: ["github"] });
const github = [];
for await (const res of iter) {
github.push({
timestamp: res.key[1],
payload: res.value,
});
}
return new Response(JSON.stringify(github, null, 2));
}
});